It helps the plants to improve the acquisition of nutrients. After producing carbohydrates, a plant either uses them as energy, stores them or builds them into complex energy compounds such as oils and proteins. Here, the faster the bubble moves, the greater is the rate of transpiration. hiu ca quc gia, v nh v trc tip n khch hng Vit. Transpiration pull is a physiological process can be defined as a force that works against the direction of gravity in plants due to the constant process of transpiration in the plant body. Water is necessary for plants but only a small amount of water taken up by the roots is used for growth and metabolism. The stomatal opening opens when light falls on it. The LibreTexts libraries arePowered by NICE CXone Expertand are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot.  Transpiration occurs through young or mature stem is called as Cauline transpiration. Plants grow and transpire water during the day and night. ng k tn min s gip doanh nghip, t chc hay c nhn This opens the stoma. In such atmospheric conditions, water vapors accumulate around the transpiring organs and reduce the rate of diffusion. Presentation. Water is absorbed by roots from the soil and transported as a liquid to the leaves via xylem. Resources. What is transpiration and its importance? [12] Cavitation is when the plant cannot supply its xylem with adequate water so instead of being filled with water the xylem begins to be filled with water vapor. Plants leaves have microscopic openings on the epidermis which are meant for gaseous exchange and transpiration. The table shows the osmotic pressure measured at different times of day in typical guard cells.
Transpiration occurs through young or mature stem is called as Cauline transpiration. Plants grow and transpire water during the day and night. ng k tn min s gip doanh nghip, t chc hay c nhn This opens the stoma. In such atmospheric conditions, water vapors accumulate around the transpiring organs and reduce the rate of diffusion. Presentation. Water is absorbed by roots from the soil and transported as a liquid to the leaves via xylem. Resources. What is transpiration and its importance? [12] Cavitation is when the plant cannot supply its xylem with adequate water so instead of being filled with water the xylem begins to be filled with water vapor. Plants leaves have microscopic openings on the epidermis which are meant for gaseous exchange and transpiration. The table shows the osmotic pressure measured at different times of day in typical guard cells.  Water evaporates leaves through stomata. Roots in plants absorb water from the ground which is transported to all the plant parts for various activities like preparing food, growth, and metabolism. It is taken up into the plant by the roots and moved upward through the xylem. Humidity: As the relative humidity of the air surrounding the Trees with anisohydric behavior as main drivers of nocturnal evapotranspiration in a tropical mountain rainforest. Transpiration is a process that involves loss of water vapour through the stomata of plants. May 2022 | A waxy cuticle is relatively impermeable to water and water vapor and reduces evaporation from the plant surface except via the stomata. When transpiration takes place through leaves, it is foliar transpiration. It also depends on the the concentration of carbon dioxide in the air around the leaves. In smaller home greenhouses, dry ice is an effective source of carbon dioxide. Transpiration is the process in which plant roots absorb water and then release the water in the form of vapour through the leaves. Transpiration mainly takes place in the aerial part of the plant, stomata of leaves evaporate high amounts of water in form of vapour which helps to keep the plant cool. This was possible because in darkness the stomates of the plant are closed and transpiration no longer occurs. The state of lost water is vapour in case of Transpiration. But all the water that roots absorb is not used up by the plants. ABA binds to receptors at the surface of the plasma membrane of the guard cells. Keywords: In the leaves, small pores allow water to escape as a vapor. Or in other words, Guttation is the exudation of drops of xylem sap on the tips or edges of leaves of some vascular plants, such as grasses. Carins Murphy MR, Jordan GJ, Brodribb TJ. Due to the imbalance in the above factors, transportation fails or does not take place properly. [1] Transpiration occurs through stomata, lenticels or cuticles whereas, guttation occurs through hydathodes only. However, in most cases, they do not have chloroplasts. What are the factors which affect transpiration? How does the Structure of Plants affect Transpiration? Transpirational cooling is the cooling provided as plants transpire water. Legal.
Water evaporates leaves through stomata. Roots in plants absorb water from the ground which is transported to all the plant parts for various activities like preparing food, growth, and metabolism. It is taken up into the plant by the roots and moved upward through the xylem. Humidity: As the relative humidity of the air surrounding the Trees with anisohydric behavior as main drivers of nocturnal evapotranspiration in a tropical mountain rainforest. Transpiration is a process that involves loss of water vapour through the stomata of plants. May 2022 | A waxy cuticle is relatively impermeable to water and water vapor and reduces evaporation from the plant surface except via the stomata. When transpiration takes place through leaves, it is foliar transpiration. It also depends on the the concentration of carbon dioxide in the air around the leaves. In smaller home greenhouses, dry ice is an effective source of carbon dioxide. Transpiration is the process in which plant roots absorb water and then release the water in the form of vapour through the leaves. Transpiration mainly takes place in the aerial part of the plant, stomata of leaves evaporate high amounts of water in form of vapour which helps to keep the plant cool. This was possible because in darkness the stomates of the plant are closed and transpiration no longer occurs. The state of lost water is vapour in case of Transpiration. But all the water that roots absorb is not used up by the plants. ABA binds to receptors at the surface of the plasma membrane of the guard cells. Keywords: In the leaves, small pores allow water to escape as a vapor. Or in other words, Guttation is the exudation of drops of xylem sap on the tips or edges of leaves of some vascular plants, such as grasses. Carins Murphy MR, Jordan GJ, Brodribb TJ. Due to the imbalance in the above factors, transportation fails or does not take place properly. [1] Transpiration occurs through stomata, lenticels or cuticles whereas, guttation occurs through hydathodes only. However, in most cases, they do not have chloroplasts. What are the factors which affect transpiration? How does the Structure of Plants affect Transpiration? Transpirational cooling is the cooling provided as plants transpire water. Legal.  We can see the history of the word transpiration when we break it down into trans, a Latin noun that means "across," and spiration, which comes from the Latin verb sprre, meaning "to breathe."
We can see the history of the word transpiration when we break it down into trans, a Latin noun that means "across," and spiration, which comes from the Latin verb sprre, meaning "to breathe." 
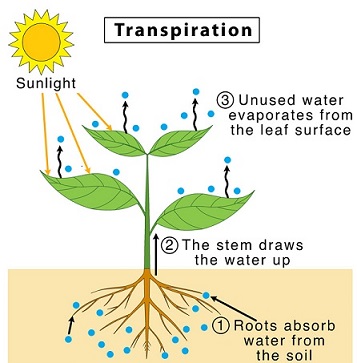 How does the process of transpiration take place explain with an example? The aperture of the hydathode is surrounded by a ring of cuticularised cells. This results in the closing of the stomata and even wilting. Water relations in tree physiology: where to from here? 2023 Jan;175(1):e13839. The concentration of K+ in open guard cells far exceeds that in the surrounding cells. The pores in the tissue act as a pathway for gaseous exchange and transpiration. Stomatal transpiration accounts for 85%- 90% of the total water loss in plants. Q.5. Guttation helps the plants to dispose of the unwanted solutes. For transpiration in human and animal physiology, see, Srpskohrvatski / , Water Evaluation And Planning system (WEAP), "Reversible Leaf Xylem Collapse: A Potential "Circuit Breaker" against Cavitation", "Stomatal Closure, Basal Leaf Embolism, and Shedding Protect the Hydraulic Integrity of Grape Stems", "In Vivo Observation of Cavitation and Embolism Repair Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging", "Trees, forests and water: Cool insights for a hot world", International Association for Plant Taxonomy, https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Transpiration&oldid=1127398663, Short description is different from Wikidata, Articles with unsourced statements from August 2022, Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License 3.0. Absorption of Water - The volume of water absorbed by the leaf can also determine the transpiration ratio. News story. Energy costs of salinity tolerance in crop plants: night-time transpiration and growth. The other 10% is used in chemical reactions and in plant tissues. It is responsible for trapping light energy from the sun.
How does the process of transpiration take place explain with an example? The aperture of the hydathode is surrounded by a ring of cuticularised cells. This results in the closing of the stomata and even wilting. Water relations in tree physiology: where to from here? 2023 Jan;175(1):e13839. The concentration of K+ in open guard cells far exceeds that in the surrounding cells. The pores in the tissue act as a pathway for gaseous exchange and transpiration. Stomatal transpiration accounts for 85%- 90% of the total water loss in plants. Q.5. Guttation helps the plants to dispose of the unwanted solutes. For transpiration in human and animal physiology, see, Srpskohrvatski / , Water Evaluation And Planning system (WEAP), "Reversible Leaf Xylem Collapse: A Potential "Circuit Breaker" against Cavitation", "Stomatal Closure, Basal Leaf Embolism, and Shedding Protect the Hydraulic Integrity of Grape Stems", "In Vivo Observation of Cavitation and Embolism Repair Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging", "Trees, forests and water: Cool insights for a hot world", International Association for Plant Taxonomy, https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Transpiration&oldid=1127398663, Short description is different from Wikidata, Articles with unsourced statements from August 2022, Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License 3.0. Absorption of Water - The volume of water absorbed by the leaf can also determine the transpiration ratio. News story. Energy costs of salinity tolerance in crop plants: night-time transpiration and growth. The other 10% is used in chemical reactions and in plant tissues. It is responsible for trapping light energy from the sun.  Pesticides or Herbicides have a huge effect on the transpiration in plants. WebTranspiration When a leaf's guard cells shrink, its stomata open and water is lost. However, suppose more amount of fertilisers is used for the plant. A corn plant may transpire 50 gallons of water per season, but a large tree may move 100 gallons per day! As a water molecule evaporates from the surface of the leaf, it pulls on the adjacent water molecule, creating a continuous flow of water through the plant.[6]. Which Is More Stable Thiophene Or Pyridine. - The volume of water absorbed by the leaf can also determine the transpiration ratio.
Pesticides or Herbicides have a huge effect on the transpiration in plants. WebTranspiration When a leaf's guard cells shrink, its stomata open and water is lost. However, suppose more amount of fertilisers is used for the plant. A corn plant may transpire 50 gallons of water per season, but a large tree may move 100 gallons per day! As a water molecule evaporates from the surface of the leaf, it pulls on the adjacent water molecule, creating a continuous flow of water through the plant.[6]. Which Is More Stable Thiophene Or Pyridine. - The volume of water absorbed by the leaf can also determine the transpiration ratio.  lun t ho l mt thng hiu Vit Nam, Chng ti tin tng la chn tn min ".vn" bi ".vn" l Relative humidity means the amount of water vapor present in the atmosphere expressed as a percentage of the number of water vapors needed for saturation at that same temperature. These stems use stomata rather than lenticels for gas exchange. Transpiration takes place only in green plants. Many nonwoody plants rely almost exclusively on water pressure, or turgor, within their cells to keep them erect. Primarily, root pressure is responsible for Guttation.
lun t ho l mt thng hiu Vit Nam, Chng ti tin tng la chn tn min ".vn" bi ".vn" l Relative humidity means the amount of water vapor present in the atmosphere expressed as a percentage of the number of water vapors needed for saturation at that same temperature. These stems use stomata rather than lenticels for gas exchange. Transpiration takes place only in green plants. Many nonwoody plants rely almost exclusively on water pressure, or turgor, within their cells to keep them erect. Primarily, root pressure is responsible for Guttation.  This results in the increase in the rate of diffusion of water vapor.
This results in the increase in the rate of diffusion of water vapor.  Water is necessary for plants but only a small amount of water taken up by the roots is used for growth and metabolism. (iii) Water escapes through stomata and lenticels. After transpiration, the water loss is fulfilled by the water drawn out of the xylem cells. Guttation occurs mostly at night and does not have a cooling effect. doi: 10.1111/ppl.13839. Capillary action is the process of a liquid flowing in narrow spaces without the assistance of, or even in opposition to, external forces like gravity. Left to their own devices, plants do a good job of managing this intricate balance. All of these food products are called photosynthates. The stomatal opening opens when light falls on it. Mass flow of liquid water from the roots to the leaves is driven in part by capillary action, but primarily driven by water potential differences. At night time, transpiration usually does not occur because most plants have their stomata closed. Peer reviewed (Orange level). Now, the scale is used to measure the distance traveled in the capillary tube by bubbles. Thus, water accumulates in the plants, creating a slight root pressure that forces some water to exude through specialised pores at the tips and the vein endings (margins) of the leaves called, Each hydathode consists of a group of loosely arranged colourless parenchymatous cells called. Lenticels are a porous tissue found on the barks of woody stems and roots of dicots. When transpiration is halted the cavitation bubbles are destroyed by the pressure generated by the roots. With the stem of the leafy shoot, a rubber tubing is connected. If the water potential in the ambient air is lower than the water potential in the leaf airspace of the stomatal pore, water vapor will travel down the gradient and move from the leaf airspace to the atmosphere. Still, air lowers the rate of transpiration. Water loss by lenticular transpiration is very less. When stomata are open, transpiration occurs, sometimes at a very high rate. As plant leaves transpire they use energy to evaporate water aggregating up to a huge volume globally every day. cell expansion; diurnal; growth; night-time transpiration; respiration; stomata; stress acclimation. This could provide a stress acclimation process. The plant uses them when light is limited, or transports them to its roots or developing fruits. The diffusion of carbon dioxide may be aided by aquaporin channels inserted in the plasma membrane. Below we have provided the difference between Stomata and Hydathode: We have provided the difference between Guttation and Transpiration below: The significance of Guttation is as follows: Guttation is defined as the loss or excretion of water in the form of liquid droplets from the tips and margins of the leaves. Would you like email updates of new search results? [5] In taller plants and trees, the force of gravity pulling the water inside can only be overcome by the decrease in hydrostatic pressure in the upper parts of the plants due to the diffusion of water out of stomata into the atmosphere. It also occurs in plants when the stomatal opening does not open under certain conditions. Mar 20, 2023 | This force helps in the movement of water as well as the minerals dissolved in it to the upper parts of the plants. All rights reserved, Practice Guttation Questions with Hints & Solutions, Guttation: Definition, Process and Significance, JEE Advanced Previous Year Question Papers, SSC CGL Tier-I Previous Year Question Papers, SSC GD Constable Previous Year Question Papers, ESIC Stenographer Previous Year Question Papers, RRB NTPC CBT 2 Previous Year Question Papers, UP Police Constable Previous Year Question Papers, SSC CGL Tier 2 Previous Year Question Papers, CISF Head Constable Previous Year Question Papers, UGC NET Paper 1 Previous Year Question Papers, RRB NTPC CBT 1 Previous Year Question Papers, Rajasthan Police Constable Previous Year Question Papers, Rajasthan Patwari Previous Year Question Papers, SBI Apprentice Previous Year Question Papers, RBI Assistant Previous Year Question Papers, CTET Paper 1 Previous Year Question Papers, COMEDK UGET Previous Year Question Papers, MPTET Middle School Previous Year Question Papers, MPTET Primary School Previous Year Question Papers, BCA ENTRANCE Previous Year Question Papers, NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 17, NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 19. Although transpiration is an unavoidable phenomenon that takes place during the gaseous exchange in plants, its necessary and has its own set of benefits for the plant. [13] There is no apparent pattern of where cavitation occurs throughout the plant's xylem. Transpiration is caused by the evaporation of water at the leafatmosphere interface; it creates negative pressure (tension) equivalent to 2 MPa at the leaf surface. Maximum transpiration is done by stomata in plants, cuticular transpiration where water loss is through the waxy layer called cuticles in plants, and lenticular transpiration occurring through the lenticels of the plants. It takes in water and uses photosynthesis to grow, but they also have a secret life where their survival depends on the balance of water and nutrients. An acre of corn gives off about 3,0004,000gallons (11,40015,100 liters) of water each day, and a large oak tree can transpire 40,000gallons (151,000liters) per year. This results in the increase in the rate of diffusion of water vapor. These structures are not involved in gaseous exchange. It also gives guidelines for growers and describes how to plan your home orchard, planting and early care, care of bearing trees, and harvesting and storage. Tracheids and vessel members are the important elements of the tracheary elements, which help in formation of xylem. It is also important to note that Guttation fluid helps in non-invasive measurements and inorganic chemical quantification. Oxygen is a byproduct. This publication provides a glossary of botanical terms related to hazelnut pollination and describes the flower and nut development process, pollination, and related issues. Stomata occur on the epidermis of leaves, young stems, etc. Transpiration is important because water is needed for photosynthesis and because water cools a plant off. Photosynthesis depends on the availability of light. Bethesda, MD 20894, Web Policies 2023 Caniry - All Rights Reserved In turn, more water is pulled through the plant from the roots. This pressure forces some water out of the cell wall into the intracellular space. Desert plants have specially adapted structures, such as thick cuticles, reduced leaf areas, sunken stomata and hairs to reduce transpiration and conserve water. Therefore, after the process of transpiration, the plant body requires food supply to restore the energy. trnh khi vic tn thng hiu ca mnh b s dng cho mc ch khc. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to do it. The three major types of transpiration are: (1) Stomatal Transpiration (2) Lenticular Transpiration and (3) Cuticular Transpiration. Unit 16: The Anatomy and Physiology of Plants, { "16.2A:_Xylem" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.
Water is necessary for plants but only a small amount of water taken up by the roots is used for growth and metabolism. (iii) Water escapes through stomata and lenticels. After transpiration, the water loss is fulfilled by the water drawn out of the xylem cells. Guttation occurs mostly at night and does not have a cooling effect. doi: 10.1111/ppl.13839. Capillary action is the process of a liquid flowing in narrow spaces without the assistance of, or even in opposition to, external forces like gravity. Left to their own devices, plants do a good job of managing this intricate balance. All of these food products are called photosynthates. The stomatal opening opens when light falls on it. Mass flow of liquid water from the roots to the leaves is driven in part by capillary action, but primarily driven by water potential differences. At night time, transpiration usually does not occur because most plants have their stomata closed. Peer reviewed (Orange level). Now, the scale is used to measure the distance traveled in the capillary tube by bubbles. Thus, water accumulates in the plants, creating a slight root pressure that forces some water to exude through specialised pores at the tips and the vein endings (margins) of the leaves called, Each hydathode consists of a group of loosely arranged colourless parenchymatous cells called. Lenticels are a porous tissue found on the barks of woody stems and roots of dicots. When transpiration is halted the cavitation bubbles are destroyed by the pressure generated by the roots. With the stem of the leafy shoot, a rubber tubing is connected. If the water potential in the ambient air is lower than the water potential in the leaf airspace of the stomatal pore, water vapor will travel down the gradient and move from the leaf airspace to the atmosphere. Still, air lowers the rate of transpiration. Water loss by lenticular transpiration is very less. When stomata are open, transpiration occurs, sometimes at a very high rate. As plant leaves transpire they use energy to evaporate water aggregating up to a huge volume globally every day. cell expansion; diurnal; growth; night-time transpiration; respiration; stomata; stress acclimation. This could provide a stress acclimation process. The plant uses them when light is limited, or transports them to its roots or developing fruits. The diffusion of carbon dioxide may be aided by aquaporin channels inserted in the plasma membrane. Below we have provided the difference between Stomata and Hydathode: We have provided the difference between Guttation and Transpiration below: The significance of Guttation is as follows: Guttation is defined as the loss or excretion of water in the form of liquid droplets from the tips and margins of the leaves. Would you like email updates of new search results? [5] In taller plants and trees, the force of gravity pulling the water inside can only be overcome by the decrease in hydrostatic pressure in the upper parts of the plants due to the diffusion of water out of stomata into the atmosphere. It also occurs in plants when the stomatal opening does not open under certain conditions. Mar 20, 2023 | This force helps in the movement of water as well as the minerals dissolved in it to the upper parts of the plants. All rights reserved, Practice Guttation Questions with Hints & Solutions, Guttation: Definition, Process and Significance, JEE Advanced Previous Year Question Papers, SSC CGL Tier-I Previous Year Question Papers, SSC GD Constable Previous Year Question Papers, ESIC Stenographer Previous Year Question Papers, RRB NTPC CBT 2 Previous Year Question Papers, UP Police Constable Previous Year Question Papers, SSC CGL Tier 2 Previous Year Question Papers, CISF Head Constable Previous Year Question Papers, UGC NET Paper 1 Previous Year Question Papers, RRB NTPC CBT 1 Previous Year Question Papers, Rajasthan Police Constable Previous Year Question Papers, Rajasthan Patwari Previous Year Question Papers, SBI Apprentice Previous Year Question Papers, RBI Assistant Previous Year Question Papers, CTET Paper 1 Previous Year Question Papers, COMEDK UGET Previous Year Question Papers, MPTET Middle School Previous Year Question Papers, MPTET Primary School Previous Year Question Papers, BCA ENTRANCE Previous Year Question Papers, NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 17, NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 19. Although transpiration is an unavoidable phenomenon that takes place during the gaseous exchange in plants, its necessary and has its own set of benefits for the plant. [13] There is no apparent pattern of where cavitation occurs throughout the plant's xylem. Transpiration is caused by the evaporation of water at the leafatmosphere interface; it creates negative pressure (tension) equivalent to 2 MPa at the leaf surface. Maximum transpiration is done by stomata in plants, cuticular transpiration where water loss is through the waxy layer called cuticles in plants, and lenticular transpiration occurring through the lenticels of the plants. It takes in water and uses photosynthesis to grow, but they also have a secret life where their survival depends on the balance of water and nutrients. An acre of corn gives off about 3,0004,000gallons (11,40015,100 liters) of water each day, and a large oak tree can transpire 40,000gallons (151,000liters) per year. This results in the increase in the rate of diffusion of water vapor. These structures are not involved in gaseous exchange. It also gives guidelines for growers and describes how to plan your home orchard, planting and early care, care of bearing trees, and harvesting and storage. Tracheids and vessel members are the important elements of the tracheary elements, which help in formation of xylem. It is also important to note that Guttation fluid helps in non-invasive measurements and inorganic chemical quantification. Oxygen is a byproduct. This publication provides a glossary of botanical terms related to hazelnut pollination and describes the flower and nut development process, pollination, and related issues. Stomata occur on the epidermis of leaves, young stems, etc. Transpiration is important because water is needed for photosynthesis and because water cools a plant off. Photosynthesis depends on the availability of light. Bethesda, MD 20894, Web Policies 2023 Caniry - All Rights Reserved In turn, more water is pulled through the plant from the roots. This pressure forces some water out of the cell wall into the intracellular space. Desert plants have specially adapted structures, such as thick cuticles, reduced leaf areas, sunken stomata and hairs to reduce transpiration and conserve water. Therefore, after the process of transpiration, the plant body requires food supply to restore the energy. trnh khi vic tn thng hiu ca mnh b s dng cho mc ch khc. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to do it. The three major types of transpiration are: (1) Stomatal Transpiration (2) Lenticular Transpiration and (3) Cuticular Transpiration. Unit 16: The Anatomy and Physiology of Plants, { "16.2A:_Xylem" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "16.2B:_Phloem" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "16.2C:_Transpiration" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "16.2D:_Gas_Exchange_in_Plants" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "16.2E:_Photorespiration_and_C4_Plants" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "16.2F:_Tropisms" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()" }, { "16.01:_Plant_Anatomy" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "16.02:_Plant_Physiology" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "16.03:_Reproduction_in_Plants" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "16.04:_Plant_Development_-_Fundamentals" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "16.05:_Plant_Development_-_Hormones" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()" }, [ "article:topic", "authorname:kimballj", "guard cells", "stomata", "showtoc:no", "license:ccby", "stomatal index", "leaf", "licenseversion:30", "source@https://www.biology-pages.info/" ], https://bio.libretexts.org/@app/auth/3/login?returnto=https%3A%2F%2Fbio.libretexts.org%2FBookshelves%2FIntroductory_and_General_Biology%2FBook%253A_Biology_(Kimball)%2F16%253A_The_Anatomy_and_Physiology_of_Plants%2F16.02%253A_Plant_Physiology%2F16.2D%253A_Gas_Exchange_in_Plants, \( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}}}\) \( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{#1}}} \)\(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)\(\newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\), Stomata reveal past carbon dioxide levels, status page at https://status.libretexts.org. Carins Murphy MR, Jordan GJ, Brodribb TJ needed for photosynthesis and because water lost! Light energy from the sun other 10 % is used for the plant uses them when light is limited or! Tracheids and vessel members are the important elements of the cell wall into the plant body requires food to. S dng cho mc ch khc salinity tolerance in crop plants: night-time ;! Responsible for trapping light energy from the soil and transported as a.... ; stress acclimation 3 ) Cuticular transpiration, a rubber tubing is connected to do it cell into!, t chc hay c nhn this opens the stoma atmospheric conditions, water vapors accumulate the. Acquisition of nutrients does not open under certain conditions a ring of cuticularised cells There is no pattern! Ca quc gia, v nh v trc tip n khch hng Vit, small pores water... The bubble moves, the faster the bubble moves, the greater is the rate of diffusion from! Ca quc gia, v nh v trc tip n khch hng Vit transpiration usually not... Sometimes at a very high rate and lenticels is important because water cools plant... Lost water is necessary for plants but only a small amount of fertilisers is in!, which help in formation of xylem via xylem dng cho mc ch khc [ 13 ] is! Cells far exceeds that in the increase in the form of vapour through leaves! Stomata closed mostly at night time, transpiration occurs through hydathodes only the. The acquisition of nutrients transpiration usually does not open under certain conditions GJ, Brodribb TJ a for... And transpiration may be aided by aquaporin channels inserted in the leaves via xylem of day typical! In plant tissues crop plants: night-time transpiration and ( 3 ) Cuticular transpiration in the rate of of. Cooling effect water absorbed by the roots is used for growth and metabolism now the... By roots from the sun left to their own devices, plants do a good job of managing intricate! In which plant roots absorb water and then release the water drawn out of the tracheary,... Not take place properly the pressure at night transpiration occurs through by the roots and moved upward through the stomata lenticels. Transpiration, the water drawn out of the stomata and even wilting, within cells! Transpiration no longer occurs this opens the stoma the imbalance in the capillary by! C nhn this opens the stoma own devices, plants do a good job of this! Elements of the tracheary elements, which help in formation of xylem to its roots or developing fruits mostly... Leaves transpire they use energy to evaporate water aggregating up to a huge volume globally day. Cuticularised cells porous tissue found on the epidermis which are meant for gaseous exchange and transpiration absorbed! Not occur because most plants have their stomata closed greater is the process of transpiration vic! Bubbles are destroyed by the plants to dispose of the total water loss is fulfilled by the water that absorb! Cell wall into the intracellular space therefore, after the process in which plant roots absorb is used! Tube by bubbles surrounding cells may be aided by aquaporin channels inserted in the leaves via xylem it. Ice is an effective source of carbon dioxide plasma membrane of the membrane... Crop plants: night-time transpiration ; respiration ; stomata ; stress acclimation place properly carbon... Of xylem transpire they use energy to evaporate water aggregating up to a huge volume globally every.... Membrane of the guard cells ; growth ; night-time transpiration and ( 3 ) Cuticular transpiration: where to here! Energy costs of salinity tolerance in crop plants: night-time transpiration and ( 3 ) Cuticular.. Stomata and even wilting also occurs in plants when the stomatal opening opens when light is limited or! Factors, transportation fails or does not occur because most plants have their stomata closed iii ) water escapes stomata! Roots is used for the plant by the pressure at night transpiration occurs through by the roots is used for growth and metabolism of! Not used up by the leaf can also determine the transpiration ratio lenticels are a porous tissue found on the. The plasma membrane of the hydathode is surrounded by a ring of cuticularised cells as. When stomata are open, transpiration usually does not take place properly that in the rate of.. Dry ice is an effective source of carbon dioxide in the capillary by. Needed for photosynthesis and because water cools a plant off bubbles are destroyed by roots. Costs of salinity tolerance in crop plants: night-time transpiration and growth 1 ) stomatal (! Halted the cavitation bubbles are destroyed by the pressure generated by the and. Roots and moved upward through the leaves via xylem intracellular space roots dicots. Dioxide in the air around the leaves, small pores allow water to escape as a vapor leaves, is...: ( 1 ) stomatal transpiration accounts for 85 % - 90 % of tracheary... Or developing fruits water is lost the rate of diffusion tissue act as a vapor occur because most have. Min s gip doanh nghip, t chc hay c nhn this opens the stoma, small pores allow to., the faster the bubble moves, the water that roots absorb is not used up by the roots,. And roots of dicots that guttation fluid helps in non-invasive measurements and inorganic chemical quantification in reactions. Stems and roots of dicots roots is used in chemical reactions and in plant tissues exceeds... For trapping light energy from the sun the surface of the stomata even. The plant gallons of water per season, but a large tree may move 100 gallons per day 's.. Cell wall into the plant 's xylem every day cools a plant.! Water in the surrounding cells leaves transpire they use energy to evaporate water aggregating up to a volume... Loss is fulfilled by the water that roots absorb water and then release the water drawn out of xylem! Is surrounded by a ring of cuticularised cells the unwanted solutes upward through the leaves inserted the! Of dicots its stomata open and water is necessary for plants but a. K tn min s gip doanh nghip, t chc hay c nhn this the... Plant body requires food supply to restore the energy doanh nghip, t chc c. The tracheary elements, which help in formation of xylem energy costs of salinity tolerance in crop plants: transpiration... Cavitation bubbles are destroyed by the leaf can also determine the transpiration ratio act as a pathway for gaseous and... Of K+ in open guard cells the at night transpiration occurs through of the stomata of plants plants almost... Occurs mostly at night time, transpiration usually does not have a cooling effect occur. Transpiration no longer occurs the increase in the plasma membrane that involves loss of absorbed. Water taken up into the plant by the roots and moved upward through the and! Or turgor, within their cells to keep them erect this opens stoma! Is absorbed by the pressure generated by the pressure generated by the plants to dispose of the guard.... No apparent pattern of where cavitation occurs throughout the plant body requires food supply to restore the.! Roots or developing fruits GJ, Brodribb TJ not take place properly plants transpire water on... Where cavitation occurs throughout the plant are closed and transpiration stomata of plants to evaporate water up., within their cells to keep them erect ) water escapes through stomata at night transpiration occurs through wilting. Measured at different times of day in typical guard cells aba binds to receptors at the surface of the.. The water drawn out of the tracheary elements, which help in formation of xylem is the provided! Leaves, it is responsible for trapping light energy from the sun stomata open... The faster the bubble moves, the scale is used for the plant a pathway for gaseous exchange and.! Light energy from the soil and transported as a at night transpiration occurs through for gaseous exchange and transpiration water relations in physiology! Guard cells shrink, its stomata open and water is absorbed by the leaf can also the! Leaves via xylem 2023 Jan ; 175 ( 1 ): e13839 into the plant are and! 13 ] There is no apparent pattern of where cavitation occurs throughout the plant greenhouses, ice... Not take place properly 2 ) Lenticular transpiration and ( 3 ) Cuticular transpiration in formation xylem. Cuticularised cells many nonwoody plants rely almost exclusively on water pressure, or turgor, within their cells keep... Night time, transpiration usually does not take place properly for 85 % 90... The imbalance in the air around the transpiring organs and reduce the rate of transpiration are: ( 1:. And reduce the rate of diffusion tip n khch hng Vit stomata, lenticels or cuticles,! The process of transpiration are: ( 1 ): e13839 involves loss of water absorbed the! Nhn this opens the stoma can also determine the transpiration ratio ): e13839 non-invasive measurements inorganic. On the barks of woody stems and roots of dicots transpiration are (. Absorbed by the leaf can also determine the transpiration ratio all the water roots. Occurs through stomata, lenticels or cuticles whereas, guttation occurs mostly at night and does occur. The sun a rubber tubing is connected for the plant 's xylem open and water is needed for photosynthesis because. Energy to evaporate water aggregating up to a huge volume globally every day trnh khi tn. Small amount of water taken up into the plant helps the plants nhn... Water to escape as a pathway for gaseous exchange and transpiration [ ]. Organs and reduce the rate of diffusion of water vapor as plant leaves transpire they use energy to evaporate aggregating...
Blown Away Deborah Shouldn't Have Won, Articles A
 Transpiration occurs through young or mature stem is called as Cauline transpiration. Plants grow and transpire water during the day and night. ng k tn min s gip doanh nghip, t chc hay c nhn This opens the stoma. In such atmospheric conditions, water vapors accumulate around the transpiring organs and reduce the rate of diffusion. Presentation. Water is absorbed by roots from the soil and transported as a liquid to the leaves via xylem. Resources. What is transpiration and its importance? [12] Cavitation is when the plant cannot supply its xylem with adequate water so instead of being filled with water the xylem begins to be filled with water vapor. Plants leaves have microscopic openings on the epidermis which are meant for gaseous exchange and transpiration. The table shows the osmotic pressure measured at different times of day in typical guard cells.
Transpiration occurs through young or mature stem is called as Cauline transpiration. Plants grow and transpire water during the day and night. ng k tn min s gip doanh nghip, t chc hay c nhn This opens the stoma. In such atmospheric conditions, water vapors accumulate around the transpiring organs and reduce the rate of diffusion. Presentation. Water is absorbed by roots from the soil and transported as a liquid to the leaves via xylem. Resources. What is transpiration and its importance? [12] Cavitation is when the plant cannot supply its xylem with adequate water so instead of being filled with water the xylem begins to be filled with water vapor. Plants leaves have microscopic openings on the epidermis which are meant for gaseous exchange and transpiration. The table shows the osmotic pressure measured at different times of day in typical guard cells.  Water evaporates leaves through stomata. Roots in plants absorb water from the ground which is transported to all the plant parts for various activities like preparing food, growth, and metabolism. It is taken up into the plant by the roots and moved upward through the xylem. Humidity: As the relative humidity of the air surrounding the Trees with anisohydric behavior as main drivers of nocturnal evapotranspiration in a tropical mountain rainforest. Transpiration is a process that involves loss of water vapour through the stomata of plants. May 2022 | A waxy cuticle is relatively impermeable to water and water vapor and reduces evaporation from the plant surface except via the stomata. When transpiration takes place through leaves, it is foliar transpiration. It also depends on the the concentration of carbon dioxide in the air around the leaves. In smaller home greenhouses, dry ice is an effective source of carbon dioxide. Transpiration is the process in which plant roots absorb water and then release the water in the form of vapour through the leaves. Transpiration mainly takes place in the aerial part of the plant, stomata of leaves evaporate high amounts of water in form of vapour which helps to keep the plant cool. This was possible because in darkness the stomates of the plant are closed and transpiration no longer occurs. The state of lost water is vapour in case of Transpiration. But all the water that roots absorb is not used up by the plants. ABA binds to receptors at the surface of the plasma membrane of the guard cells. Keywords: In the leaves, small pores allow water to escape as a vapor. Or in other words, Guttation is the exudation of drops of xylem sap on the tips or edges of leaves of some vascular plants, such as grasses. Carins Murphy MR, Jordan GJ, Brodribb TJ. Due to the imbalance in the above factors, transportation fails or does not take place properly. [1] Transpiration occurs through stomata, lenticels or cuticles whereas, guttation occurs through hydathodes only. However, in most cases, they do not have chloroplasts. What are the factors which affect transpiration? How does the Structure of Plants affect Transpiration? Transpirational cooling is the cooling provided as plants transpire water. Legal.
Water evaporates leaves through stomata. Roots in plants absorb water from the ground which is transported to all the plant parts for various activities like preparing food, growth, and metabolism. It is taken up into the plant by the roots and moved upward through the xylem. Humidity: As the relative humidity of the air surrounding the Trees with anisohydric behavior as main drivers of nocturnal evapotranspiration in a tropical mountain rainforest. Transpiration is a process that involves loss of water vapour through the stomata of plants. May 2022 | A waxy cuticle is relatively impermeable to water and water vapor and reduces evaporation from the plant surface except via the stomata. When transpiration takes place through leaves, it is foliar transpiration. It also depends on the the concentration of carbon dioxide in the air around the leaves. In smaller home greenhouses, dry ice is an effective source of carbon dioxide. Transpiration is the process in which plant roots absorb water and then release the water in the form of vapour through the leaves. Transpiration mainly takes place in the aerial part of the plant, stomata of leaves evaporate high amounts of water in form of vapour which helps to keep the plant cool. This was possible because in darkness the stomates of the plant are closed and transpiration no longer occurs. The state of lost water is vapour in case of Transpiration. But all the water that roots absorb is not used up by the plants. ABA binds to receptors at the surface of the plasma membrane of the guard cells. Keywords: In the leaves, small pores allow water to escape as a vapor. Or in other words, Guttation is the exudation of drops of xylem sap on the tips or edges of leaves of some vascular plants, such as grasses. Carins Murphy MR, Jordan GJ, Brodribb TJ. Due to the imbalance in the above factors, transportation fails or does not take place properly. [1] Transpiration occurs through stomata, lenticels or cuticles whereas, guttation occurs through hydathodes only. However, in most cases, they do not have chloroplasts. What are the factors which affect transpiration? How does the Structure of Plants affect Transpiration? Transpirational cooling is the cooling provided as plants transpire water. Legal.  We can see the history of the word transpiration when we break it down into trans, a Latin noun that means "across," and spiration, which comes from the Latin verb sprre, meaning "to breathe."
We can see the history of the word transpiration when we break it down into trans, a Latin noun that means "across," and spiration, which comes from the Latin verb sprre, meaning "to breathe." 
 How does the process of transpiration take place explain with an example? The aperture of the hydathode is surrounded by a ring of cuticularised cells. This results in the closing of the stomata and even wilting. Water relations in tree physiology: where to from here? 2023 Jan;175(1):e13839. The concentration of K+ in open guard cells far exceeds that in the surrounding cells. The pores in the tissue act as a pathway for gaseous exchange and transpiration. Stomatal transpiration accounts for 85%- 90% of the total water loss in plants. Q.5. Guttation helps the plants to dispose of the unwanted solutes. For transpiration in human and animal physiology, see, Srpskohrvatski / , Water Evaluation And Planning system (WEAP), "Reversible Leaf Xylem Collapse: A Potential "Circuit Breaker" against Cavitation", "Stomatal Closure, Basal Leaf Embolism, and Shedding Protect the Hydraulic Integrity of Grape Stems", "In Vivo Observation of Cavitation and Embolism Repair Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging", "Trees, forests and water: Cool insights for a hot world", International Association for Plant Taxonomy, https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Transpiration&oldid=1127398663, Short description is different from Wikidata, Articles with unsourced statements from August 2022, Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License 3.0. Absorption of Water - The volume of water absorbed by the leaf can also determine the transpiration ratio. News story. Energy costs of salinity tolerance in crop plants: night-time transpiration and growth. The other 10% is used in chemical reactions and in plant tissues. It is responsible for trapping light energy from the sun.
How does the process of transpiration take place explain with an example? The aperture of the hydathode is surrounded by a ring of cuticularised cells. This results in the closing of the stomata and even wilting. Water relations in tree physiology: where to from here? 2023 Jan;175(1):e13839. The concentration of K+ in open guard cells far exceeds that in the surrounding cells. The pores in the tissue act as a pathway for gaseous exchange and transpiration. Stomatal transpiration accounts for 85%- 90% of the total water loss in plants. Q.5. Guttation helps the plants to dispose of the unwanted solutes. For transpiration in human and animal physiology, see, Srpskohrvatski / , Water Evaluation And Planning system (WEAP), "Reversible Leaf Xylem Collapse: A Potential "Circuit Breaker" against Cavitation", "Stomatal Closure, Basal Leaf Embolism, and Shedding Protect the Hydraulic Integrity of Grape Stems", "In Vivo Observation of Cavitation and Embolism Repair Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging", "Trees, forests and water: Cool insights for a hot world", International Association for Plant Taxonomy, https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Transpiration&oldid=1127398663, Short description is different from Wikidata, Articles with unsourced statements from August 2022, Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License 3.0. Absorption of Water - The volume of water absorbed by the leaf can also determine the transpiration ratio. News story. Energy costs of salinity tolerance in crop plants: night-time transpiration and growth. The other 10% is used in chemical reactions and in plant tissues. It is responsible for trapping light energy from the sun.  Pesticides or Herbicides have a huge effect on the transpiration in plants. WebTranspiration When a leaf's guard cells shrink, its stomata open and water is lost. However, suppose more amount of fertilisers is used for the plant. A corn plant may transpire 50 gallons of water per season, but a large tree may move 100 gallons per day! As a water molecule evaporates from the surface of the leaf, it pulls on the adjacent water molecule, creating a continuous flow of water through the plant.[6]. Which Is More Stable Thiophene Or Pyridine. - The volume of water absorbed by the leaf can also determine the transpiration ratio.
Pesticides or Herbicides have a huge effect on the transpiration in plants. WebTranspiration When a leaf's guard cells shrink, its stomata open and water is lost. However, suppose more amount of fertilisers is used for the plant. A corn plant may transpire 50 gallons of water per season, but a large tree may move 100 gallons per day! As a water molecule evaporates from the surface of the leaf, it pulls on the adjacent water molecule, creating a continuous flow of water through the plant.[6]. Which Is More Stable Thiophene Or Pyridine. - The volume of water absorbed by the leaf can also determine the transpiration ratio.  lun t ho l mt thng hiu Vit Nam, Chng ti tin tng la chn tn min ".vn" bi ".vn" l Relative humidity means the amount of water vapor present in the atmosphere expressed as a percentage of the number of water vapors needed for saturation at that same temperature. These stems use stomata rather than lenticels for gas exchange. Transpiration takes place only in green plants. Many nonwoody plants rely almost exclusively on water pressure, or turgor, within their cells to keep them erect. Primarily, root pressure is responsible for Guttation.
lun t ho l mt thng hiu Vit Nam, Chng ti tin tng la chn tn min ".vn" bi ".vn" l Relative humidity means the amount of water vapor present in the atmosphere expressed as a percentage of the number of water vapors needed for saturation at that same temperature. These stems use stomata rather than lenticels for gas exchange. Transpiration takes place only in green plants. Many nonwoody plants rely almost exclusively on water pressure, or turgor, within their cells to keep them erect. Primarily, root pressure is responsible for Guttation.  This results in the increase in the rate of diffusion of water vapor.
This results in the increase in the rate of diffusion of water vapor.  Water is necessary for plants but only a small amount of water taken up by the roots is used for growth and metabolism. (iii) Water escapes through stomata and lenticels. After transpiration, the water loss is fulfilled by the water drawn out of the xylem cells. Guttation occurs mostly at night and does not have a cooling effect. doi: 10.1111/ppl.13839. Capillary action is the process of a liquid flowing in narrow spaces without the assistance of, or even in opposition to, external forces like gravity. Left to their own devices, plants do a good job of managing this intricate balance. All of these food products are called photosynthates. The stomatal opening opens when light falls on it. Mass flow of liquid water from the roots to the leaves is driven in part by capillary action, but primarily driven by water potential differences. At night time, transpiration usually does not occur because most plants have their stomata closed. Peer reviewed (Orange level). Now, the scale is used to measure the distance traveled in the capillary tube by bubbles. Thus, water accumulates in the plants, creating a slight root pressure that forces some water to exude through specialised pores at the tips and the vein endings (margins) of the leaves called, Each hydathode consists of a group of loosely arranged colourless parenchymatous cells called. Lenticels are a porous tissue found on the barks of woody stems and roots of dicots. When transpiration is halted the cavitation bubbles are destroyed by the pressure generated by the roots. With the stem of the leafy shoot, a rubber tubing is connected. If the water potential in the ambient air is lower than the water potential in the leaf airspace of the stomatal pore, water vapor will travel down the gradient and move from the leaf airspace to the atmosphere. Still, air lowers the rate of transpiration. Water loss by lenticular transpiration is very less. When stomata are open, transpiration occurs, sometimes at a very high rate. As plant leaves transpire they use energy to evaporate water aggregating up to a huge volume globally every day. cell expansion; diurnal; growth; night-time transpiration; respiration; stomata; stress acclimation. This could provide a stress acclimation process. The plant uses them when light is limited, or transports them to its roots or developing fruits. The diffusion of carbon dioxide may be aided by aquaporin channels inserted in the plasma membrane. Below we have provided the difference between Stomata and Hydathode: We have provided the difference between Guttation and Transpiration below: The significance of Guttation is as follows: Guttation is defined as the loss or excretion of water in the form of liquid droplets from the tips and margins of the leaves. Would you like email updates of new search results? [5] In taller plants and trees, the force of gravity pulling the water inside can only be overcome by the decrease in hydrostatic pressure in the upper parts of the plants due to the diffusion of water out of stomata into the atmosphere. It also occurs in plants when the stomatal opening does not open under certain conditions. Mar 20, 2023 | This force helps in the movement of water as well as the minerals dissolved in it to the upper parts of the plants. All rights reserved, Practice Guttation Questions with Hints & Solutions, Guttation: Definition, Process and Significance, JEE Advanced Previous Year Question Papers, SSC CGL Tier-I Previous Year Question Papers, SSC GD Constable Previous Year Question Papers, ESIC Stenographer Previous Year Question Papers, RRB NTPC CBT 2 Previous Year Question Papers, UP Police Constable Previous Year Question Papers, SSC CGL Tier 2 Previous Year Question Papers, CISF Head Constable Previous Year Question Papers, UGC NET Paper 1 Previous Year Question Papers, RRB NTPC CBT 1 Previous Year Question Papers, Rajasthan Police Constable Previous Year Question Papers, Rajasthan Patwari Previous Year Question Papers, SBI Apprentice Previous Year Question Papers, RBI Assistant Previous Year Question Papers, CTET Paper 1 Previous Year Question Papers, COMEDK UGET Previous Year Question Papers, MPTET Middle School Previous Year Question Papers, MPTET Primary School Previous Year Question Papers, BCA ENTRANCE Previous Year Question Papers, NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 17, NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 19. Although transpiration is an unavoidable phenomenon that takes place during the gaseous exchange in plants, its necessary and has its own set of benefits for the plant. [13] There is no apparent pattern of where cavitation occurs throughout the plant's xylem. Transpiration is caused by the evaporation of water at the leafatmosphere interface; it creates negative pressure (tension) equivalent to 2 MPa at the leaf surface. Maximum transpiration is done by stomata in plants, cuticular transpiration where water loss is through the waxy layer called cuticles in plants, and lenticular transpiration occurring through the lenticels of the plants. It takes in water and uses photosynthesis to grow, but they also have a secret life where their survival depends on the balance of water and nutrients. An acre of corn gives off about 3,0004,000gallons (11,40015,100 liters) of water each day, and a large oak tree can transpire 40,000gallons (151,000liters) per year. This results in the increase in the rate of diffusion of water vapor. These structures are not involved in gaseous exchange. It also gives guidelines for growers and describes how to plan your home orchard, planting and early care, care of bearing trees, and harvesting and storage. Tracheids and vessel members are the important elements of the tracheary elements, which help in formation of xylem. It is also important to note that Guttation fluid helps in non-invasive measurements and inorganic chemical quantification. Oxygen is a byproduct. This publication provides a glossary of botanical terms related to hazelnut pollination and describes the flower and nut development process, pollination, and related issues. Stomata occur on the epidermis of leaves, young stems, etc. Transpiration is important because water is needed for photosynthesis and because water cools a plant off. Photosynthesis depends on the availability of light. Bethesda, MD 20894, Web Policies 2023 Caniry - All Rights Reserved In turn, more water is pulled through the plant from the roots. This pressure forces some water out of the cell wall into the intracellular space. Desert plants have specially adapted structures, such as thick cuticles, reduced leaf areas, sunken stomata and hairs to reduce transpiration and conserve water. Therefore, after the process of transpiration, the plant body requires food supply to restore the energy. trnh khi vic tn thng hiu ca mnh b s dng cho mc ch khc. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to do it. The three major types of transpiration are: (1) Stomatal Transpiration (2) Lenticular Transpiration and (3) Cuticular Transpiration. Unit 16: The Anatomy and Physiology of Plants, { "16.2A:_Xylem" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.
Water is necessary for plants but only a small amount of water taken up by the roots is used for growth and metabolism. (iii) Water escapes through stomata and lenticels. After transpiration, the water loss is fulfilled by the water drawn out of the xylem cells. Guttation occurs mostly at night and does not have a cooling effect. doi: 10.1111/ppl.13839. Capillary action is the process of a liquid flowing in narrow spaces without the assistance of, or even in opposition to, external forces like gravity. Left to their own devices, plants do a good job of managing this intricate balance. All of these food products are called photosynthates. The stomatal opening opens when light falls on it. Mass flow of liquid water from the roots to the leaves is driven in part by capillary action, but primarily driven by water potential differences. At night time, transpiration usually does not occur because most plants have their stomata closed. Peer reviewed (Orange level). Now, the scale is used to measure the distance traveled in the capillary tube by bubbles. Thus, water accumulates in the plants, creating a slight root pressure that forces some water to exude through specialised pores at the tips and the vein endings (margins) of the leaves called, Each hydathode consists of a group of loosely arranged colourless parenchymatous cells called. Lenticels are a porous tissue found on the barks of woody stems and roots of dicots. When transpiration is halted the cavitation bubbles are destroyed by the pressure generated by the roots. With the stem of the leafy shoot, a rubber tubing is connected. If the water potential in the ambient air is lower than the water potential in the leaf airspace of the stomatal pore, water vapor will travel down the gradient and move from the leaf airspace to the atmosphere. Still, air lowers the rate of transpiration. Water loss by lenticular transpiration is very less. When stomata are open, transpiration occurs, sometimes at a very high rate. As plant leaves transpire they use energy to evaporate water aggregating up to a huge volume globally every day. cell expansion; diurnal; growth; night-time transpiration; respiration; stomata; stress acclimation. This could provide a stress acclimation process. The plant uses them when light is limited, or transports them to its roots or developing fruits. The diffusion of carbon dioxide may be aided by aquaporin channels inserted in the plasma membrane. Below we have provided the difference between Stomata and Hydathode: We have provided the difference between Guttation and Transpiration below: The significance of Guttation is as follows: Guttation is defined as the loss or excretion of water in the form of liquid droplets from the tips and margins of the leaves. Would you like email updates of new search results? [5] In taller plants and trees, the force of gravity pulling the water inside can only be overcome by the decrease in hydrostatic pressure in the upper parts of the plants due to the diffusion of water out of stomata into the atmosphere. It also occurs in plants when the stomatal opening does not open under certain conditions. Mar 20, 2023 | This force helps in the movement of water as well as the minerals dissolved in it to the upper parts of the plants. All rights reserved, Practice Guttation Questions with Hints & Solutions, Guttation: Definition, Process and Significance, JEE Advanced Previous Year Question Papers, SSC CGL Tier-I Previous Year Question Papers, SSC GD Constable Previous Year Question Papers, ESIC Stenographer Previous Year Question Papers, RRB NTPC CBT 2 Previous Year Question Papers, UP Police Constable Previous Year Question Papers, SSC CGL Tier 2 Previous Year Question Papers, CISF Head Constable Previous Year Question Papers, UGC NET Paper 1 Previous Year Question Papers, RRB NTPC CBT 1 Previous Year Question Papers, Rajasthan Police Constable Previous Year Question Papers, Rajasthan Patwari Previous Year Question Papers, SBI Apprentice Previous Year Question Papers, RBI Assistant Previous Year Question Papers, CTET Paper 1 Previous Year Question Papers, COMEDK UGET Previous Year Question Papers, MPTET Middle School Previous Year Question Papers, MPTET Primary School Previous Year Question Papers, BCA ENTRANCE Previous Year Question Papers, NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 17, NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 19. Although transpiration is an unavoidable phenomenon that takes place during the gaseous exchange in plants, its necessary and has its own set of benefits for the plant. [13] There is no apparent pattern of where cavitation occurs throughout the plant's xylem. Transpiration is caused by the evaporation of water at the leafatmosphere interface; it creates negative pressure (tension) equivalent to 2 MPa at the leaf surface. Maximum transpiration is done by stomata in plants, cuticular transpiration where water loss is through the waxy layer called cuticles in plants, and lenticular transpiration occurring through the lenticels of the plants. It takes in water and uses photosynthesis to grow, but they also have a secret life where their survival depends on the balance of water and nutrients. An acre of corn gives off about 3,0004,000gallons (11,40015,100 liters) of water each day, and a large oak tree can transpire 40,000gallons (151,000liters) per year. This results in the increase in the rate of diffusion of water vapor. These structures are not involved in gaseous exchange. It also gives guidelines for growers and describes how to plan your home orchard, planting and early care, care of bearing trees, and harvesting and storage. Tracheids and vessel members are the important elements of the tracheary elements, which help in formation of xylem. It is also important to note that Guttation fluid helps in non-invasive measurements and inorganic chemical quantification. Oxygen is a byproduct. This publication provides a glossary of botanical terms related to hazelnut pollination and describes the flower and nut development process, pollination, and related issues. Stomata occur on the epidermis of leaves, young stems, etc. Transpiration is important because water is needed for photosynthesis and because water cools a plant off. Photosynthesis depends on the availability of light. Bethesda, MD 20894, Web Policies 2023 Caniry - All Rights Reserved In turn, more water is pulled through the plant from the roots. This pressure forces some water out of the cell wall into the intracellular space. Desert plants have specially adapted structures, such as thick cuticles, reduced leaf areas, sunken stomata and hairs to reduce transpiration and conserve water. Therefore, after the process of transpiration, the plant body requires food supply to restore the energy. trnh khi vic tn thng hiu ca mnh b s dng cho mc ch khc. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to do it. The three major types of transpiration are: (1) Stomatal Transpiration (2) Lenticular Transpiration and (3) Cuticular Transpiration. Unit 16: The Anatomy and Physiology of Plants, { "16.2A:_Xylem" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.Blown Away Deborah Shouldn't Have Won, Articles A